There are tons of hair color products today, each offering a different result. But before scheduling an appointment with your hairstylist, this time to color your hair, it’s best to understand the difference between hair dye and henna.
That’s what this article is all about—hair dye vs henna. Read on to learn how chemical hair dyes and henna differ in composition, how they work, results, and effects.
Regular Hair Dye and Its Composition

Hair color refers to hair dyes and bleaches applied to hair to give it a different color from its natural one. These consist primarily of:
- An oxidizing agent, commonly known as a developer, such as ammonium and potassium persulfate and hydrogen peroxide
- A dye precursor (often referred to as a base): It’s an alkalizing agent (ammonia). For ammonia-free products, it’s ethanolamines.
- Coupler or modifier: This comes in the same bottle as the base. The modifier reacts with the now oxidized base (imine) to form a color after it’s mixed with a developer.
Once you’ve applied the dye, the color deposits on the hair. This occurs when the bleaching agent eliminates natural hair color.
Henna and Its Composition

Henna is an herbal hair color. It’s a unique product as the only hair color with 100% natural ingredients.
You obtain henna powder from dried and ground leaves of the Lawsonia Inermis plant. The Lawsone molecules in the henna responsible for dying get released when mixed with natural acids like vinegar or lemon juice, resulting in a vibrant red-orange hair shade.
Differences Between Hair Dye and Henna
With a clear understanding of the distinction between hair dye and henna, it’s easier to choose the product that would work better for you in your current situation. Here is a comparison between hair dye and henna.
1. Working
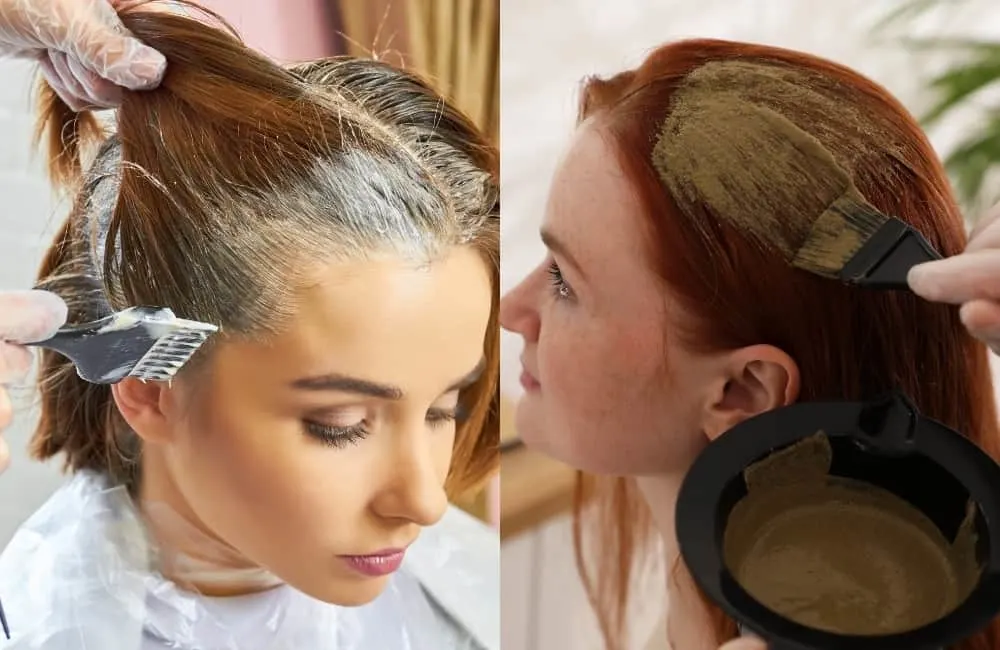

Temporary dye works by coating each strand with color.
Permanent hair dye bonds with the hair after the base (ammonia) opens up the hair cuticle scale-like cells and gets to the hair cortex. The developer then strips the natural hair color of melanin. This bleaching agent also sets off chemical reactions that oxidize and deposit the new hair color onto your hair cuticles.
Unlike non-permanent and semi-permanent hair dyes, the permanent chemical dye can withstand numerous washes. The new hair color doesn’t fade away whatsoever. But there’s a caveat to this remarkable color retention. These hair dyes damage the cuticle and reduce the moisture in the hair, making it highly susceptible to dryness and damage.
On the other hand, henna is a natural hair coloring product. What happens is the paste you form after mixing the henna with a natural acid is what you use to coat the hair shaft.
Then, natural red coloring lawsone gradually moves from the henna into the shaft via gaps in the cuticle, binding with keratin and strengthening your cuticles. The result is naturally colored hair that settles and deepens if you apply the henna repeatedly.
2. Results
Hair dye (especially the permanent one) works to produce different colors on all hair types. The hair color you get does not wash out at any given time. Nevertheless, some fading may occur with time, but using products specifically designed for color-treated hair can minimize this.
Naturally, you can expect new growth of typically half an inch every month. Hence you’ll need to do regular touch-ups every four to six weeks.
The result you get from henna hair coloring depends on your hair type and the amount of time you expose it to the henna. The longer the exposure time, the deeper the red.
You can liken the process to placing a teabag on a white cloth. It gets stained, and the longer you leave the teabag there, the darker the stain. Also, lighter natural hair will get a more vibrant red.
Although henna is considered permanent, it requires that you color from time to time.
3. Effects on the Scalp
Hair dyes can induce the following effects on your scalp:
- Dryness, actinic keratosis, and inflammation of scalp: You can develop wax-like bumpy skin growths
- Loss of moisture balance, resulting in sebum secretion
- Damage to hair matrix cells. This alters the hair growth cycle, on top of deteriorating the hair growth environment.
Henna component, on the other hand, has the following positive effects on the scalp:
- It moisturizes and protects the scalp
- It helps maintain a clean scalp
- Prevents inflammation
- Acts as an antioxidant that boosts the hair growth environment
Overall, while henna prevents the hair and scalp from deteriorating, hair dye usually accelerates the condition.
4. Effects on Hair
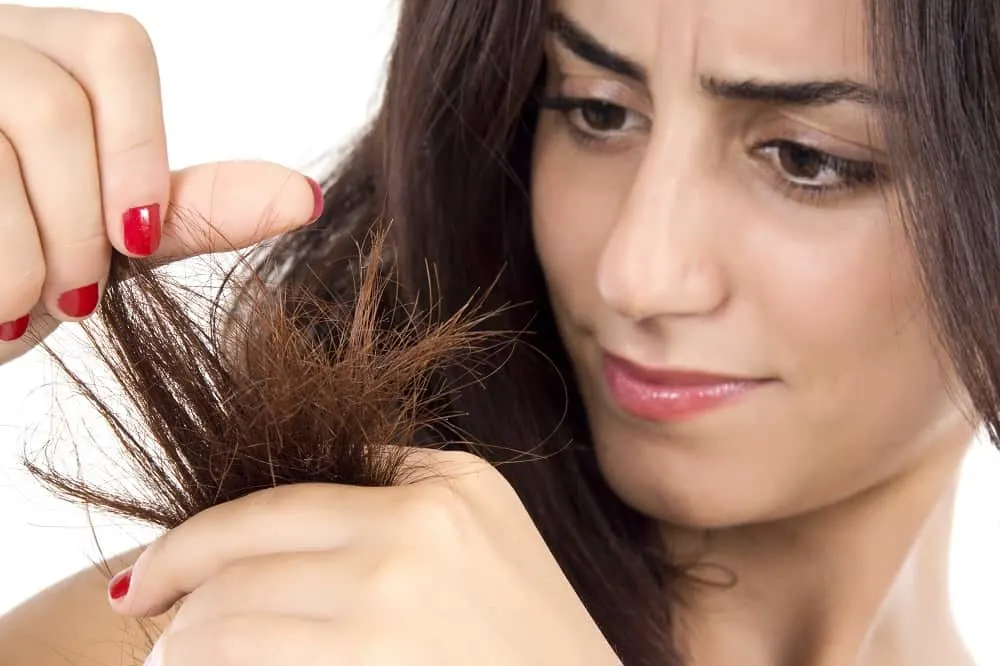

Much as it brings about excellent color development, this comes with a price. It damages and disintegrates the hair cuticles. The sole cause of this is the harsh chemicals present in the product. Hair dye also strips hair of moisture content, resulting in dry ends and, in most cases, split-ends.
Unlike hair dye, henna strengthens the hair. Additionally, it boosts the hair’s moisture retention capacity.
With the protective hair oils of the hair cuticles intact, body, volume, and luster increase. And what’s more, the coloring component in henna bonds with hair, giving more stability to color and coloration.
Whether you’re looking to color your hair or you’re a salon owner who specializes in hair color, you can use this information to decide on whether to use henna to dye hair or hair coloring products.
Hair dyes produce excellent color development, but they require you to exercise extra caution and use high-quality hair care products. Henna contains no chemicals as it’s made from 100% natural products, meaning it can cause no damage to hair. Just be sure that it’s all-natural.
