It’s normal for your natural hair to turn grey and white as you grow older. But how can you differentiate between grey and white hair?
The color of your natural hair results from the melanin in the hair follicles. Depending on your ethnicity, your hair can be black, blonde, brown, or red. With age, the pigment cells (melanocytes) that produce melanin begin to die, and hair changes to grey and eventually white.
We’ll discuss the differences between grey and white hair in detail to help you understand what sets them apart.
What Shade Is Grey Hair?
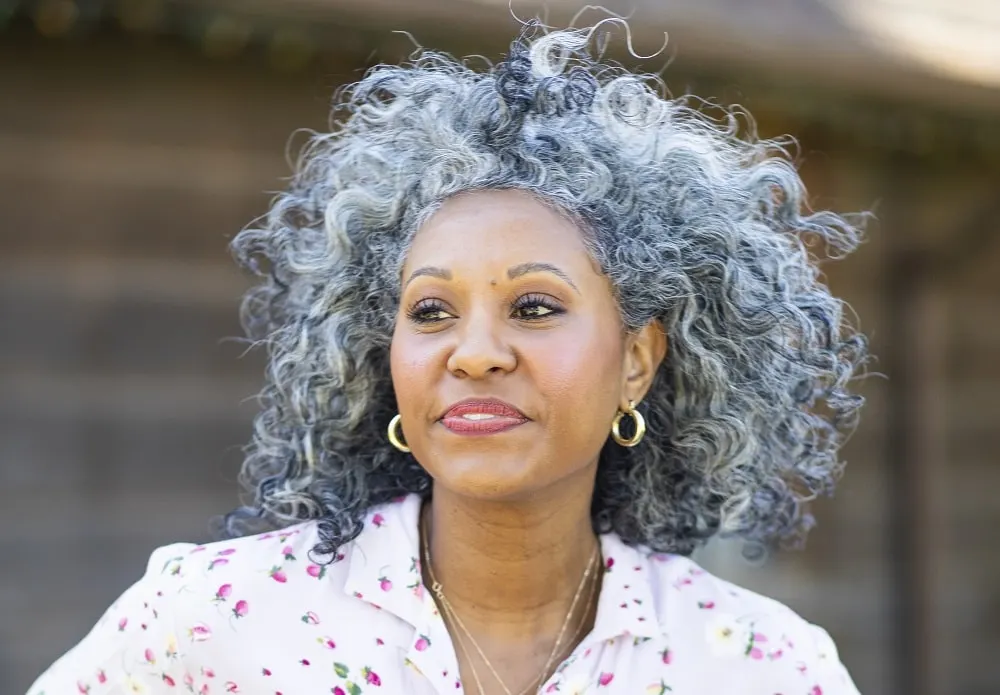

Grey hair appears light-colored but with darker shades. This color is due to the combination of naturally-colored hair and white hair. When melanocytes in some hair follicles begin to die, they fail to produce melanin. As a result, hair strands lose their natural hue and turn white.
The remaining melanocytes in the other hair follicles continue producing melanin resulting in naturally colored hair strands. Grey hair is a mixture of naturally-colored hair and white hair.
Genes are the major determiners of when hair starts to turn grey. However, premature greying may occur due to various illnesses, stress, and smoking tobacco.
What Shade Is White Hair?
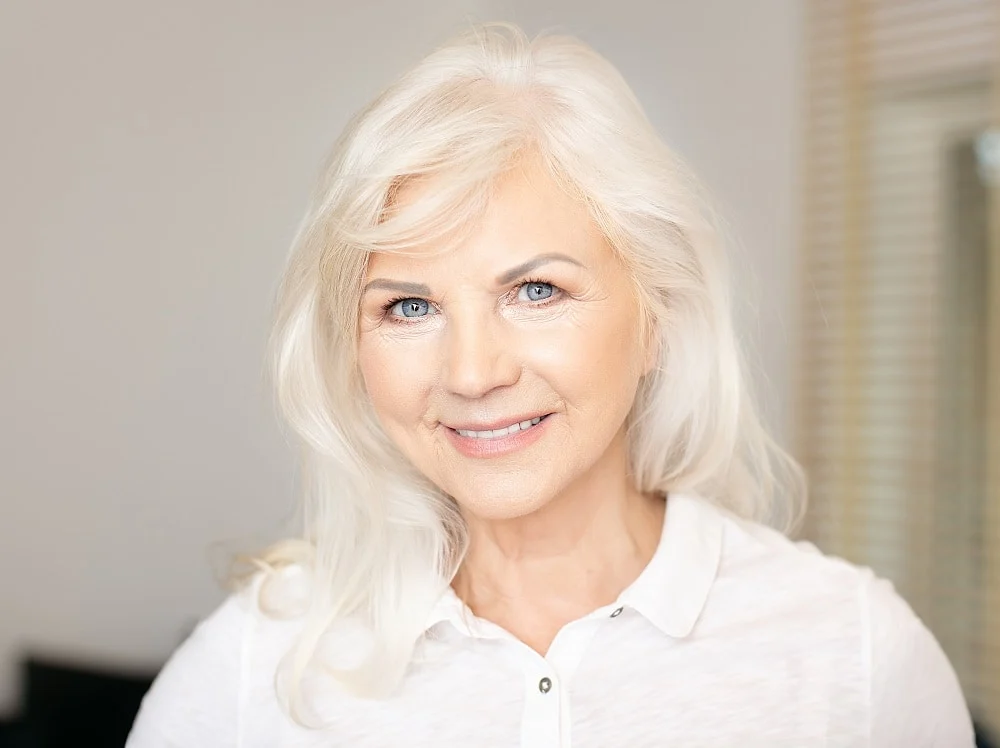

Unlike grey hair, white hair is lighter than platinum blonde. When no more melanin-producing cells are in your hair follicles, your hair turns white. Hair follicles fail to produce new melanocytes, causing your hair to lose its natural color
People sometimes use the terms white hair, silver hair, and grey hair to refer to any hair that has lost natural color or pigment.
What Does White Hair and Grey Hair Look Like?
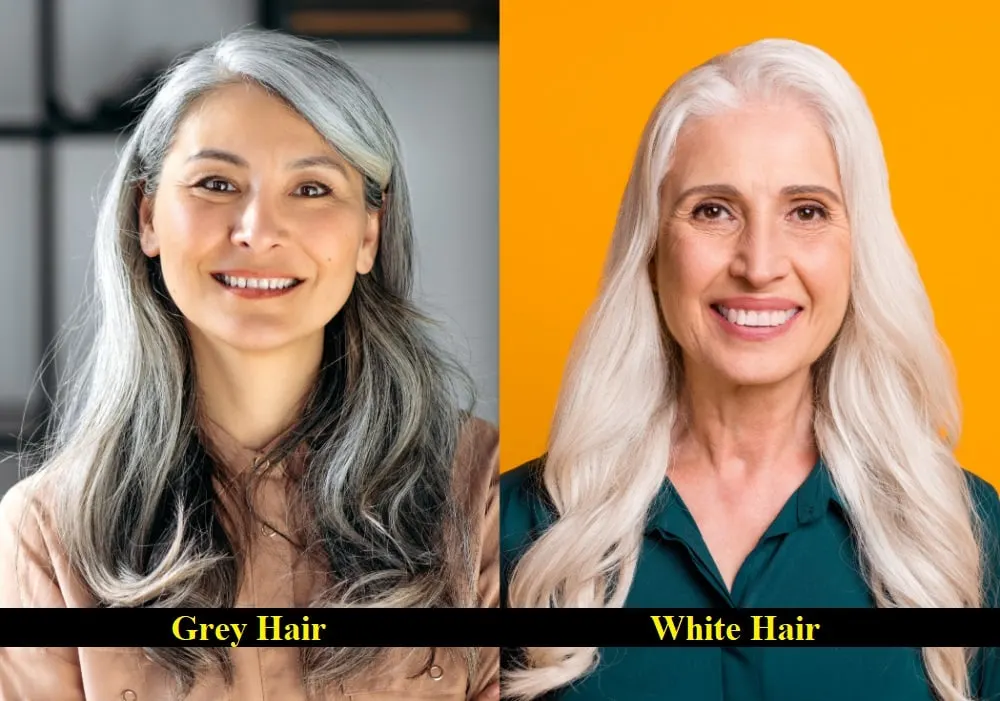

White hair is lighter than grey hair. The difference in color between the two types of hair is due to the presence or absence of melanin in hair follicles. If you have grey hair, some of your hair follicles have active melanin remaining. This melanin is responsible for the naturally-colored hair strands.
On the other hand, white hair means the absence of melanin in the hair follicles. With no remaining melanin, your hair loses its natural color and turns completely white.
Key Differences Between Grey and White Hair
Structure
The main difference between grey and white hair is in structure. Grey hair is a mixture of naturally-colored hair and white hair. The hair looks light-colored but with darker shades. People refer to it as salt and pepper hair (a mix of black, gray, and silver hair).
You may also find some grey hair strands that appear white at the base but are colored at the end part. Hair turns more grey as white hair grows.
White hair lacks naturally-colored hair strands, making the hair look lighter than platinum blonde hair.
Formation
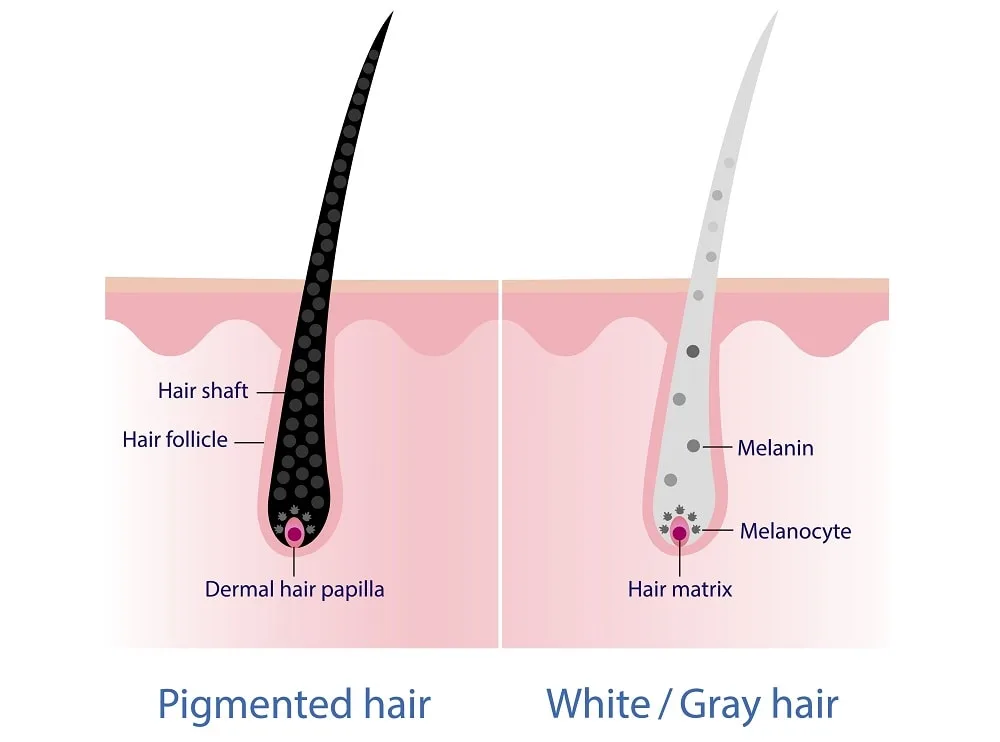
Melanin in hair follicles gives hair its natural color. Since hair color differs in people of different ethnic groups, you may wonder what causes these differences.
Melanin can be divided into eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin causes hair to acquire a black or dark brown color. The more eumelanin you have, the darker your hair is. Pheomelanin makes hair develop red and blonde shades.
When eumelanin or pheomelanin in some of your hair follicles dies, the affected hair turns grey. You’ll still have naturally-colored hair strands where melanin is active. White hair forms when all your hair follicles lose eumelanin or pheomelanin. That means you no longer have melanin to give your hair its natural color.
Causes
Thanks to genetics, your hair might start to turn grey earlier than everybody else’s. If people in your family grow grey hair in their 30s, you’re also likely to have grey hair in your 30s.
Health conditions, including thyroid disease, vitamin B-12 deficiency, tuberous sclerosis, vitiligo, alopecia areata, and neurofibromatosis, can cause premature greying. Other triggers are stress and tobacco smoking.
When your hair starts to grey due to genetics, health issues, stress, and tobacco smoking, it eventually turns white.
Age of Occurrence

Most people see their hair turning grey in their mid-30s or 40s. If greying results from genetics, illness, stress, or smoking tobacco, your hair might begin to grey in your mid-20s.
Below is the average age of onset based on ethnicity:
- Caucasian: Mid-30s
- Asian: Late 30s
- Black: Mid-40s
Once your hair turns grey, it takes about ten years to turn completely white.
Texture
Your white hair may feel coarser, drier, and wirier if you touch it. This means your hair follicles no longer produce melanin and enough sebum. Your hair follicles naturally produce sebum (oil) that hydrates your hair. Dehydrated white hair will have a different texture from naturally-colored hair.
On the other hand, grey hair consists of white and naturally-colored hair that’s yet to turn grey. As a result, your hair might have a mixed texture due to the coarse, dry, and wiry white hair and fine, medium, or thick naturally-colored hair.
Below is a grey vs white hair comparison table showing how grey hair differs from white hair.
| Parameter | Grey Hair | White Hair |
| Structure | A mixture of naturally colored hair and white hair | Completely white hair |
| Formation | Lack of melanin in some hair follicles | Loss of melanin in all hair follicles |
| Causes | Genetics, age, health conditions, stress, and smoking tobacco | Genetics, age, health conditions, stress, and smoking tobacco |
| Age of occurrence | Mid-30s or 40s | 10 years after the hair turns grey |
| Texture | Coarse, dry, and wiry depending on the degree of greying | Coarser, drier, and wirier |
Conclusion
You can now tell the difference between grey and white hair. If you have started going grey, it means melanin in some hair follicles is dying, causing some hair strands to turn white.
On the other hand, white hair means the absence of melanin in your hair follicles. When this happens, all your hair turns completely white. You can always use various styling colors and moisturizers to keep your grey or white hair soft, shiny, and in your desired color.
FAQs
Here are the most common questions you may run into regarding grey and white hair.
Blondes go white, although some blondes turn to light blond while others appear darker and duller due to the emergence of white hair. Unlike naturally dark hair, blonde hair turns white more quickly due to the little pheomelanin.
The grey or white hair is due to the presence/absence of melanin in hair follicles. People with grey hair have little melanin remaining, while those with white hair have no melanin.
Once your hair turns grey or white due to genetics or age, you cannot reverse it. At this stage, your hair follicles no longer produce melanin and can’t regain that capability.
