You can discover what hair color is dominant between black or brown by understanding its makeup. Hair color depends on the phenotypic modification of genes. The shaft, hair cuticle, and bulb represent the main structures of a single hair. One type of cell inside the hair bulb directly impacts hair color.
Melanocytes give you a variety of hair colors and dictate which hue is prominent. Continue reading to learn more.
Black Vs. Brown: Which Hair Color Is Dominant?
When it comes to genetics, black hair is usually considered the dominant trait over brown hair.
Hair color is determined by melanin, a pigment produced by cells called melanocytes. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin, responsible for black and brown hair colors, and pheomelanin, which gives rise to red and yellow hues.
Although black hair is often seen as dominant, hair color inheritance is a complex process involving multiple genes. These genes can interact with each other and the environment, creating a wide range of hair colors and shades. As a result, predicting hair color in offspring can be challenging, leading to various hair shades within a family.
It’s important to note that dominant and recessive traits are not fixed and can change over generations due to gene mutations or selection pressures. This means that the question of which hair color is dominant may not have a definitive answer, as hair color inheritance is a dynamic process influenced by various genetic and environmental factors.
In summary, while black hair is generally considered dominant over brown hair, the complex interplay of multiple genes and environmental factors can result in a wide variety of hair colors and shades. Dominance in hair color is not fixed and can evolve over time, making the inheritance of hair color a fascinating and intricate process.
How Hair Color Is Determined
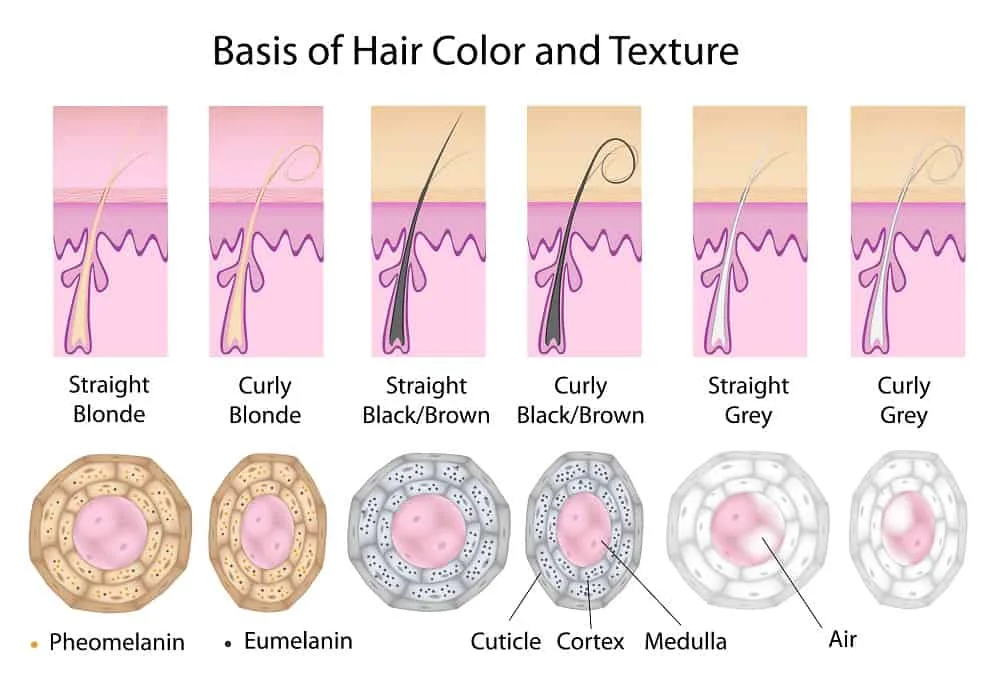
The gene named MC1R represents a single class of melanin and determines the pigmentation of a hair follicle and its corresponding color. The more pigment produced, the darker the hair and vice versa. Discover the three types of melanin below.
Eumelanin
The gene MC1R, when in an active condition, produces eumelanin. Eumelanin protects the skin from damage by sunlight. People who produce high levels of eumelanin tend to display dark tones.
Pheomelanin
When in an inactive state, MC1R produces pheomelanin. Unlike eumelanin, pheomelanin does not protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation. People with high amounts of pheomelanin have reddish or blond hair.
Neuromelanin
Neuromelanin can be found in the brain. Neurodegenerative disorders, like Parkinson’s Disease, sometimes occur due to the mutation of neuromelanin. Parkinson’s bears an indirect relation to hair color.
What Hair Color Is Dominant?
Genes determine which of the five different colors a person will display. Blonde and red hair results from recessive genes, while black and brown hair remains genetically dominant.
#1. Black
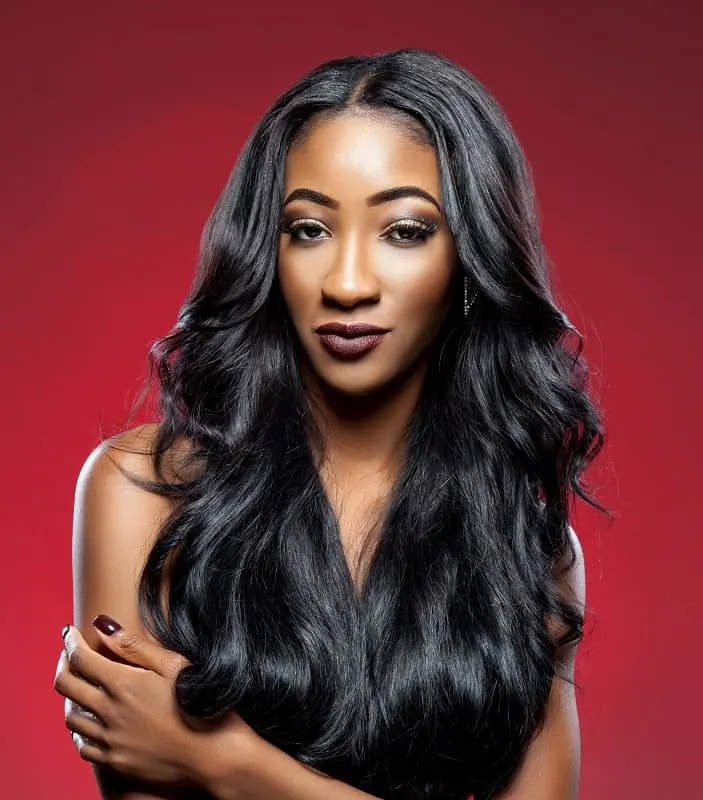

Black hair is the most common and genetically dominant hair color in the world. It contains a high concentration of eumelanin, which gives it a dark and rich appearance.
Black hair is predominantly found in people of African, Asian, and some Mediterranean descent because they have lower levels of tyrosinase in their bodies. Tyrosinase is an enzyme that plays a key role in melanin production.
Black hair is the most common hair color globally, with over 75% of the world’s population having this hair color.
#2. Brown
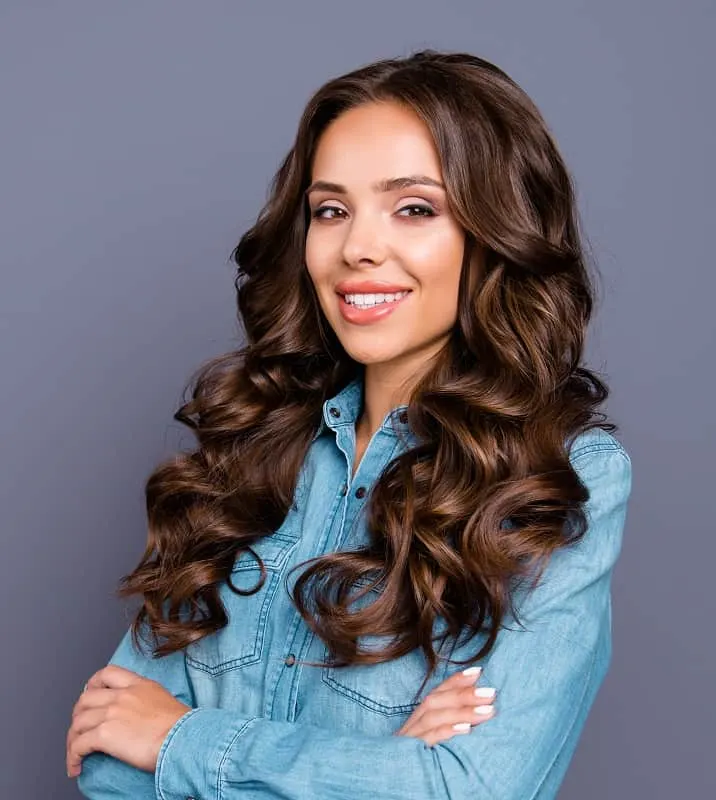

Brown hair is also considered genetically dominant and comes in a variety of shades, from light brown to dark brown. It’s characterized by a higher amount of eumelanin and a lower level of pheomelanin.
People inherit the MC1R gene from parents with brown hair, which produces a higher amount of eumelanin and lower levels of pheomelanin. Brown hair is most prevalent in people of European descent but can also be found in other populations worldwide.
#3. Blonde
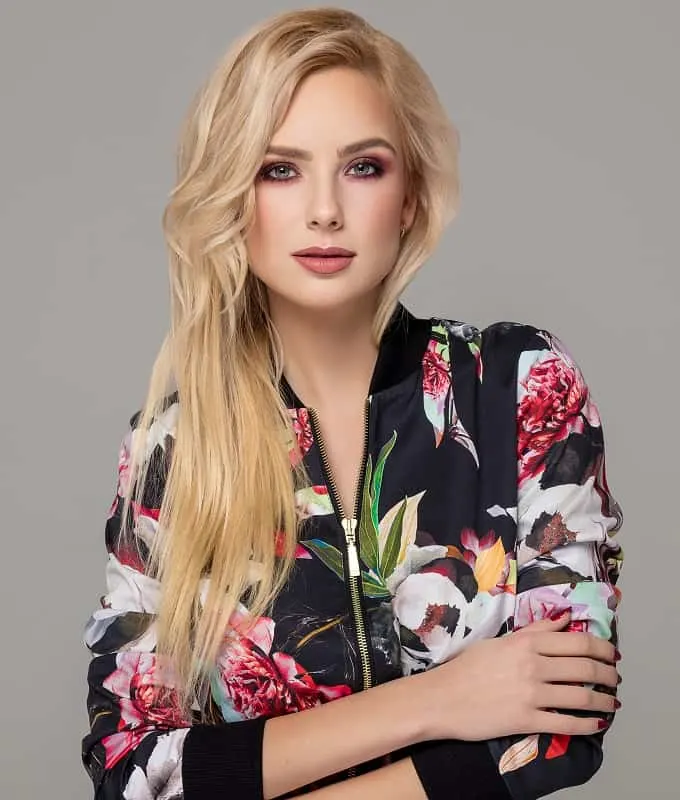

Blonde hair is a recessive trait and results from a lower concentration of eumelanin and pheomelanin pigments. Strawberry blonde consists of a high level of pheomelanin. The mutation of the single-nucleotide polymorphisms or the adenine guanine nucleotides represents a potential contributing factor to the blonde hair phenotype.
Blonde hair is more common in people of European descent, particularly in Northern European populations.
#4. Red
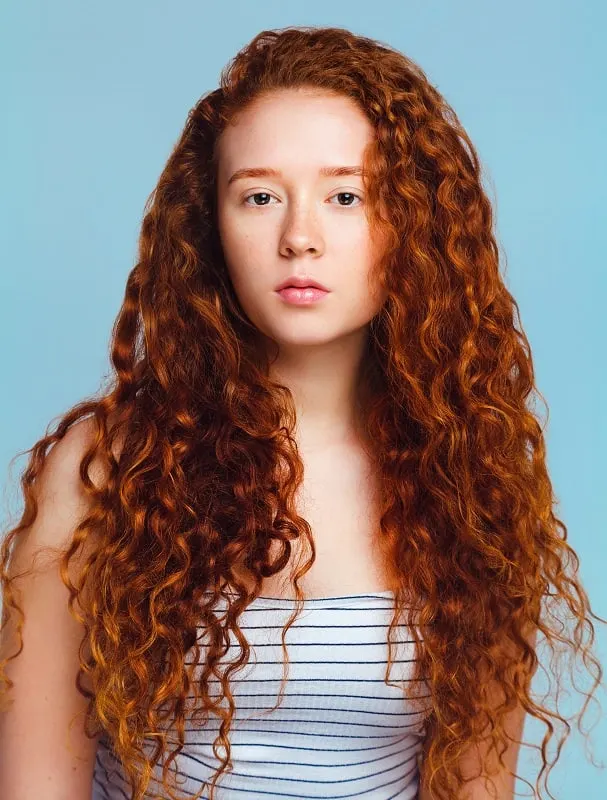

Red hair is another recessive trait and is caused by a mutation on the MC1R gene on chromosome 16. This rare hair color results from high levels of pheomelanin and low levels of eumelanin. Red hair is most commonly found in people with Celtic origins, such as those from Scotland and Ireland. Only about 1-2% of the global population has red hair.
White or Gray
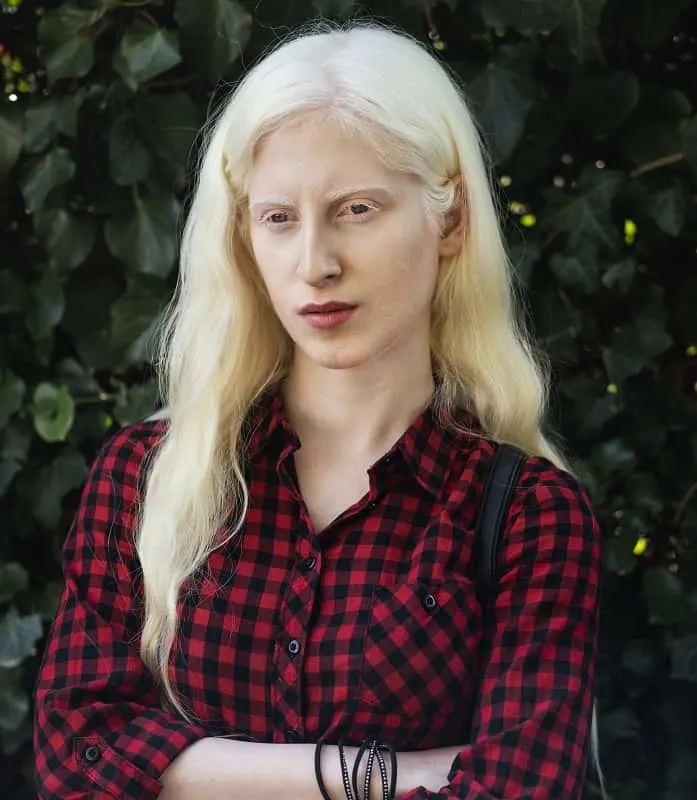

White hair or gray hair does not have pheomelanin and eumelanin pigments. Patients with albinism, a rare skin pigment disorder, display white hair. Gray hair, on the other hand, results from a decrease in melanin production as we age, causing the hair to lose its natural color.
Related Topics
